Odin is our deep UV resonant Raman spectrometer, and continued testing shows it consistently delivers game-changing performance when measuring biopharma products. The unit is compact and easy to use while depositing high laser energies at the target, and the system has an additional advantage when measuring fragile samples.
Operating in the deep UV can lead to very high energies being deposited onto samples. This can result in damage, which consequently degrades the spectra obtained as the target material is degraded. Immunoglobulin (IgG), which is known to be relatively prone to UV degradation, was examined using Odin to assess this effect and the effect of Odin.
IgG is a common type of antibody found in 75 % of serum antibodies within humans. IgG has been previously measured by a number of authors working within the deep UV Raman field and thus is an excellent material to assess the instrument’s ability. For this experiment, the sample concentration of IgG was 1 mg/ml in water.
The data was acquired using 30-second integration times and an average of 10 frames to extract the spectra. The Odin HES spectrometer design allows a larger spot to be deposited at the target, reducing power density (600 µm diameter in this case).
IgG spectra were obtained in three different measurement conditions:
- Static; such that the same region of the sample was continuously exposed to the laser
- Rotating: with the sample rotating, tracing an approx. 15mm circle over the sample surface
- Rotating and linearly translating, as above, with the addition of a 15mm ‘to-and-fro’ linear motion to ensure no part of the sample had extended laser exposure.
The resulting spectra are given in Figure 1. In the static configuration, the spectra indicate that considerable damage has occurred to the sample, with no clear peaks being present between 700 cm-1 and 1500 cm-1. Using a rotation stage improves the data quality obtained, with peaks now becoming prominent in this region. However, many peaks are 2-3 times weaker than the structure observed above 1500 cm-1. The addition of the linear stage considerably enhances the spectral quality indicating no damage is observed within the timeframe of the measurement. These spectra have had no post-processing applied and are superior to many currently published in the literature. This indicates that the larger spot combined with the motion applied to the target eliminates damage to the sample during the observation period.
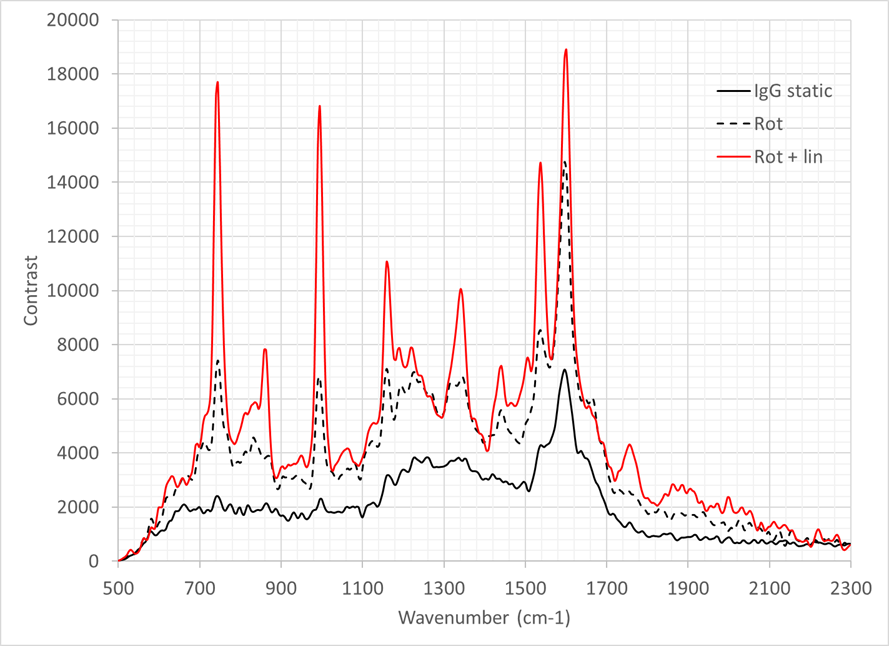
Figure 1. Raman spectra of IgG (30 second integration time, average of 10 frames). Solid black line = IgG is measured in static configuration; Dotted black line IgG measured with sample rotating during the observation; Red line = IgG measured with a complex motion applied using a rotation and linear stage
Read the paper “Demonstration of a compact deep UV Raman spatial heterodyne spectrometer for biologics analysis”, Foster et al (2022)
To find out more about Odin: please contact mfoster@zoodesigndev3.co.uk